Power transformers are devices used to transport electrical power without changing the frequency from one circuit to another. They function according to the electromagnetic mutual induction theory. They are employed in the electrical power transmission process between primary distribution circuits and generators. In distribution networks, voltage is stepped up or down using power transformers. The electrical system that powers this equipment uses alternating current (AC). Power transformers are regarded as static devices because they do not have any rotating or moving components. Read More…
With more than 500 current transformer manufacturers in the world, Triad Magnetics realizes you have a choice. Why choose Triad? Having served the needs of many industries for more than half a century, Triad believes its experience makes the difference. And if there is one point experience has taught it, it is that it must remain flexible and adaptable to the changing needs of the market.
At CES Transformers, we dedicate ourselves to designing and manufacturing high-quality electric transformers that power industrial, commercial, and utility applications across the nation. We take pride in combining advanced engineering with decades of hands-on expertise to deliver reliable performance and lasting value. Every transformer we build reflects our commitment to precision, safety, and...

At Spang Engineered Solutions, we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-performance electric transformers that meet the demands of today’s advanced power and control systems. We take pride in engineering solutions that go beyond standard components, combining innovation and precision to deliver superior magnetic and electronic performance.

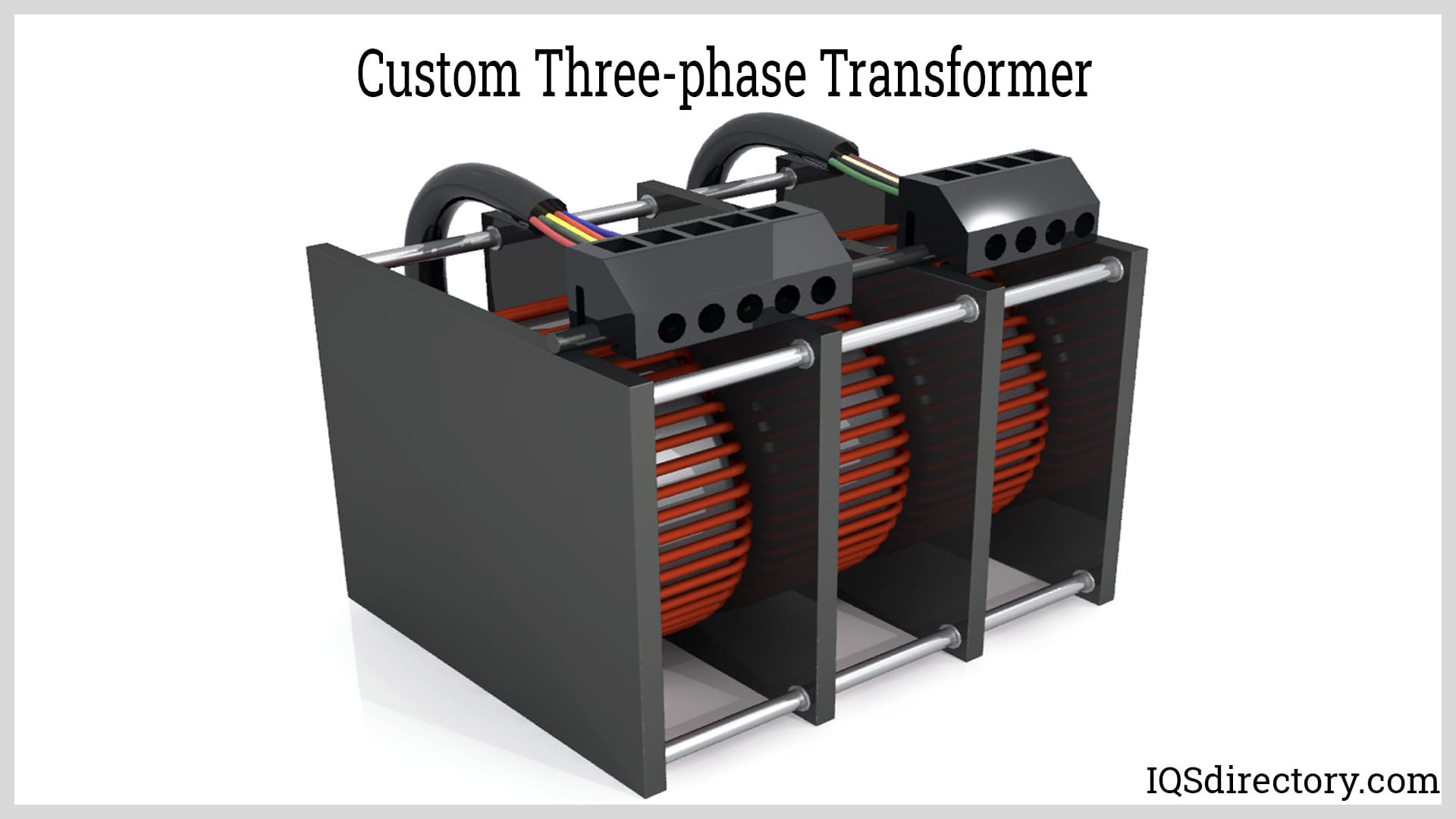
Established in 1973 manufacturing a wide variety of custom transformers and inductors. Transformer products range from small PC transformers to single-phase units with capacities between 10mW and 25KVA, as well as three-phase transformers from 7VA to 75KVA.

At Olsun Electrics Corporation, we specialize in crafting high-quality electric transformers designed to meet the diverse needs of our customers. Our expertise extends to providing comprehensive solutions that encompass design, manufacturing, and testing, ensuring that every transformer we produce delivers exceptional performance and reliability.
More Power Transformer Manufacturers

Power transformers are crucial for preventing significant energy losses caused by Joule's effect when transmitting large amounts of electrical power across long distances. They do this by turning the power into a high-voltage current and then stepping it down to a low-voltage current, which is safer. As a result, they can frequently be found in industrial facilities, power plants, and electric utility businesses. According to their ranges, power transformers can be categorized as large, medium, or low-power transformers.
- Transformers with medium power might vary from -100MVA.
- Low-power transformers can range in size from 500 to 7,500 kVA.
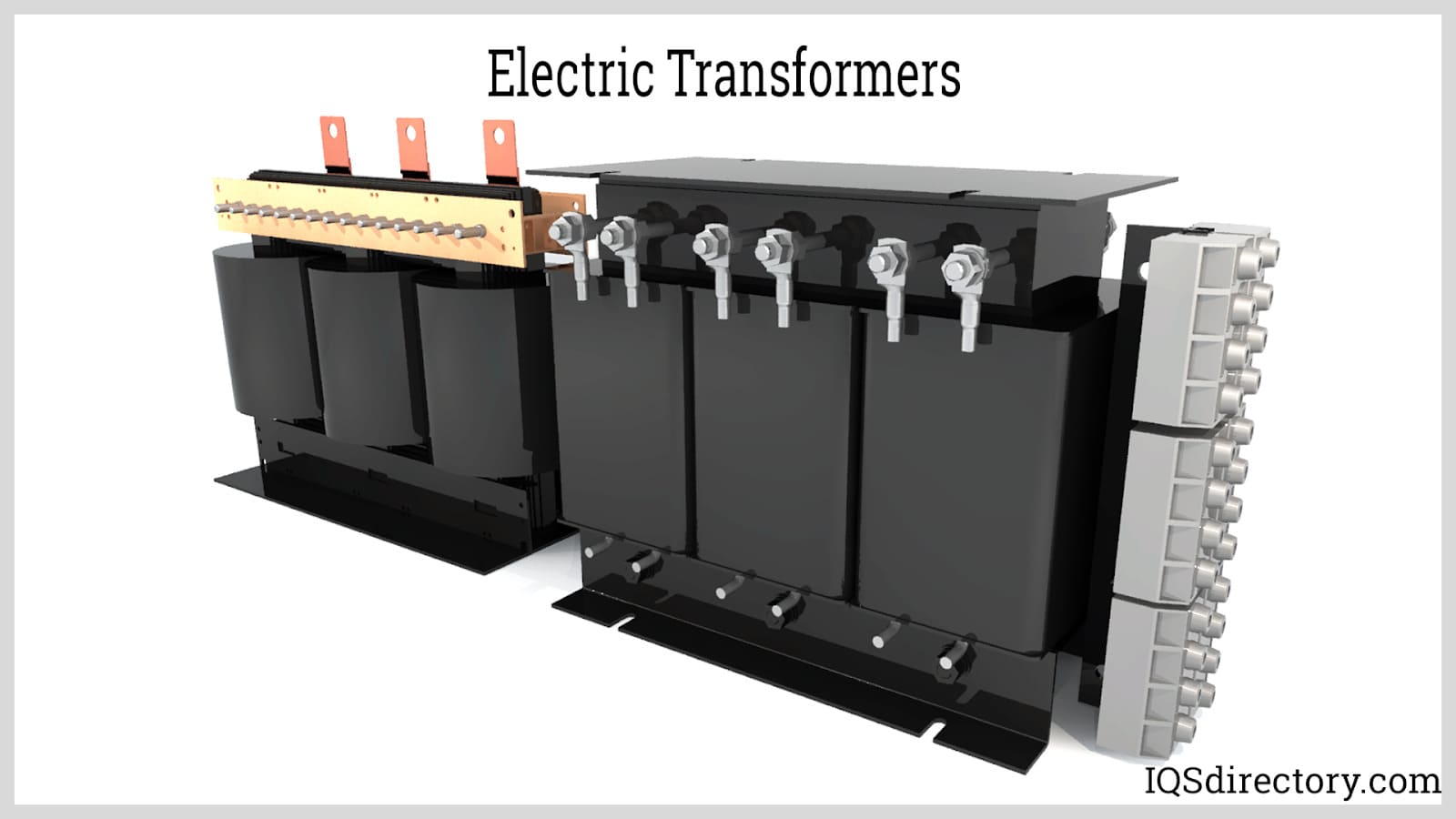
Components of Power Transformers
The basic components of a power transformer include the core, tap changer, insulating material, and primary and secondary windings.
Core Components
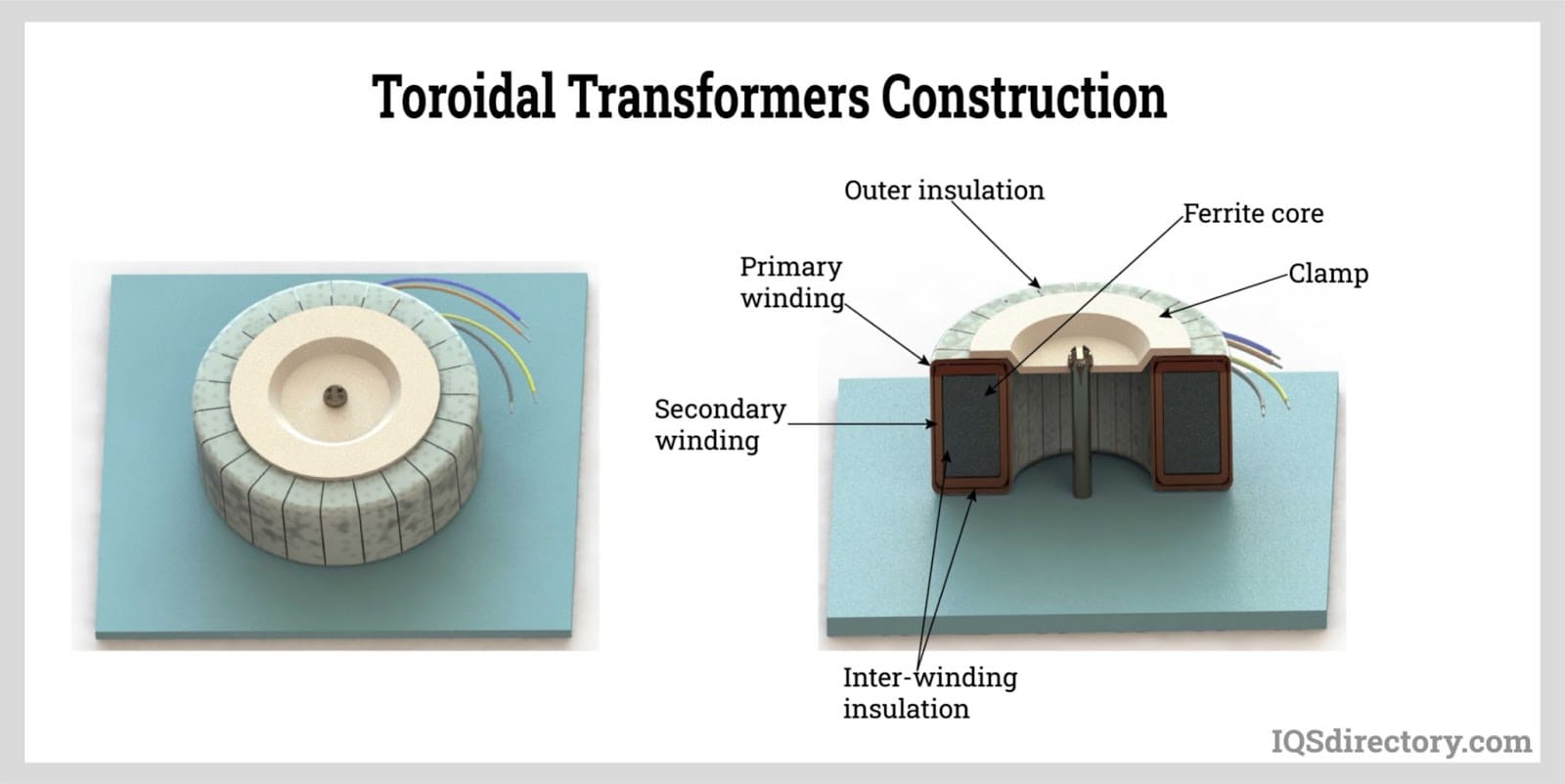
The core is structural support for the windings and a low-reluctance channel for the magnetic flux. Thin steel sheets are laminated and stacked to create them. A covering separates the sheets from one another. The iron or steel sheets are typically less than 1 millimeter thick, and their carbon content is kept below 0.1% to minimize hysteresis and eddy current losses. The eddy current is further diminished by incorporating silicon into the steel alloy. Limbs are the vertical portions of the core where the windings are carried, and yokes are the horizontal portions of the core that join the limbs.

Primary and Secondary Windings
The primary winding is to which the input voltage is applied, and the winding to which the output voltage is supplied is known as the secondary winding. The primary and secondary windings can function as either low-voltage (LV) or high-voltage (HV) winding. Compared to low-voltage winding, high-voltage winding has more turns and is made of a thinner conductor. The low-voltage winding contains fewer turns. Given that the low voltage winding carries a higher current than the high voltage winding, it has a thicker conductor than the high voltage winding.
A specific number of turns of copper or aluminum conductor coil make up the windings. Due to its high electrical conductivity and flexibility, copper is ideal since it requires less winding and is simpler to wrap around the core.
Tap Changer
Tap changers adjust the number of turns in one winding to control the transformer's output voltage as it responds to the fluctuating input voltage and load. The turn ratio is altered as a result of this alteration. The output voltage rises when unloading occurs and falls when the system is loaded. In the HV winding, tap changers are often attached to perform precise voltage adjustments and reduce core losses in the transformer.
Tap changers come in two varieties. On-load tap changers are made to tap the voltage without interfering with the current passage to the load. Offload tap changers need to operate with the transformer's load disconnected.
Bushings
Bushings are sealed barriers that house the terminal connecting the extremities of the transformer windings to the current-carrying cable from an electrical network—usually constructed of porcelain or epoxy resin, bushing insulation. They are usually mounted above the main tank.

The following are additional power transformer components:
- Insulating materials
- Transformer tank
- Conservator component
- Cooling system
- Explosion vent
- Buchholz relay
Power Transformer Operating Principle
The electromagnetic induction law of Faraday is the basis for how power transformers work. All transformers, generators, motors, inductors, and solenoids operate according to this law.
According to Faraday's law, applying a closed loop to a fluctuating magnetic field causes an electromotive force (emf) to be generated across the closed loop. An alternating or fluctuating magnetic flux surrounds a coil when an alternating current is allowed to pass through it in the primary winding. A ferromagnetic core is necessary for the primary winding's magnetic flux to transfer to a secondary winding successfully. Due to electromagnetic induction, the magnetic flux will then cause an emf in the secondary winding. The secondary winding's current will be stimulated by the produced emf.

The induced voltage on the secondary winding can be connected to the input voltage on the primary winding. This is because the voltage for each turn of the primary and secondary windings is the same. The voltage output is lower than the input voltage. When the number of turns on the secondary winding is less than that of the main winding, we have a step-down transformer. The voltage output is greater than the input voltage. If the total number of turns in the secondary coil exceeds that in the primary coil, it is termed a step-up transformer.
Types of Power Transformers
The construction of the core and windings, phases, turns ratio, and core material can all be used to categorize power transformers.
Power transformers based on phases include:
- Autotransformers
- Three-phase transformers
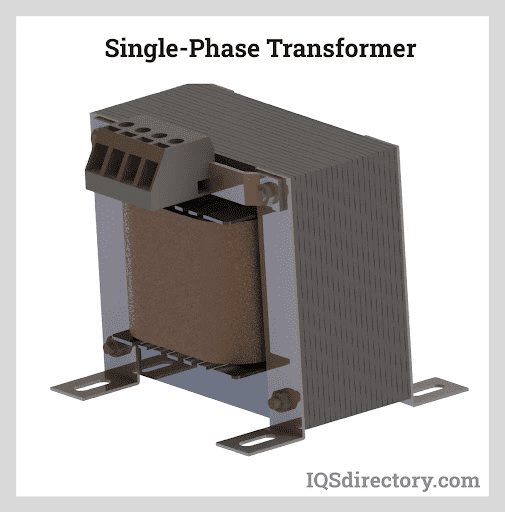
- Single-phase transformer
Power transformers based on turns ratio include:
- Step-up transformer
- Step-down transformer
- Isolation transformer
Power transformers based on core material include:
- Air core transformer
- Iron core transformer
- Toroidal core transformer
- Ferrite core transformer
Choosing the Right Power Transformer Manufacturer
To ensure the most positive outcome when purchasing power transformers from a power transformer manufacturer, it is important to compare several businesses using our directory of power transformer manufacturers. Each power transformer company has a business profile page highlighting their areas of experience and capabilities, along with a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each power transformer business website using our patented website previewer for a better idea of what each business specializes in. Then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple power transformer companies with the same form.










 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services