The Zig Zag transformer, also known as "interconnected star winding," is a special-purpose transformer used in power systems. It acts as a barrier between the ground and the component, preventing the system component from being damaged by fault currents. Read More…
With more than 500 current transformer manufacturers in the world, Triad Magnetics realizes you have a choice. Why choose Triad? Having served the needs of many industries for more than half a century, Triad believes its experience makes the difference. And if there is one point experience has taught it, it is that it must remain flexible and adaptable to the changing needs of the market.
At CES Transformers, we dedicate ourselves to designing and manufacturing high-quality electric transformers that power industrial, commercial, and utility applications across the nation. We take pride in combining advanced engineering with decades of hands-on expertise to deliver reliable performance and lasting value. Every transformer we build reflects our commitment to precision, safety, and...

At Spang Engineered Solutions, we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-performance electric transformers that meet the demands of today’s advanced power and control systems. We take pride in engineering solutions that go beyond standard components, combining innovation and precision to deliver superior magnetic and electronic performance.

Established in 1973 manufacturing a wide variety of custom transformers and inductors. Transformer products range from small PC transformers to single-phase units with capacities between 10mW and 25KVA, as well as three-phase transformers from 7VA to 75KVA.

At Olsun Electrics Corporation, we specialize in crafting high-quality electric transformers designed to meet the diverse needs of our customers. Our expertise extends to providing comprehensive solutions that encompass design, manufacturing, and testing, ensuring that every transformer we produce delivers exceptional performance and reliability.
More Zig Zag Transformer Manufacturers
What is a Zig Zag Transformer?
A zig zag transformer is a specialized type of electrical transformer that plays a crucial role in power system grounding, harmonic mitigation, and voltage stabilization. By terminating harmonics and providing a path for zero-sequence currents, zig zag transformers help maintain power quality, enhance electrical safety, and ensure the reliability of distribution networks. These transformers are engineered to address unique challenges that arise in three-phase systems, especially where a neutral connection must be established or improved.
In modern electrical engineering, zig zag transformers are essential for applications such as fault protection, neutral grounding, and unbalanced load compensation. Their unique winding configuration—combining both star (Y) and delta connections—enables them to effectively suppress third-harmonic currents, reduce voltage stress during ground faults, and support power system stability in both industrial and utility settings.
How a Zig Zag Transformer Functions
Unlike conventional power transformers, a zig zag transformer is not primarily used for voltage transformation between two different levels. Instead, its innovative winding design provides electrical benefits such as grounding, harmonic suppression, and unbalanced load management. The zig zag connection is an interleaved winding scheme that merges the characteristics of both star (Y) and delta (Δ) configurations.
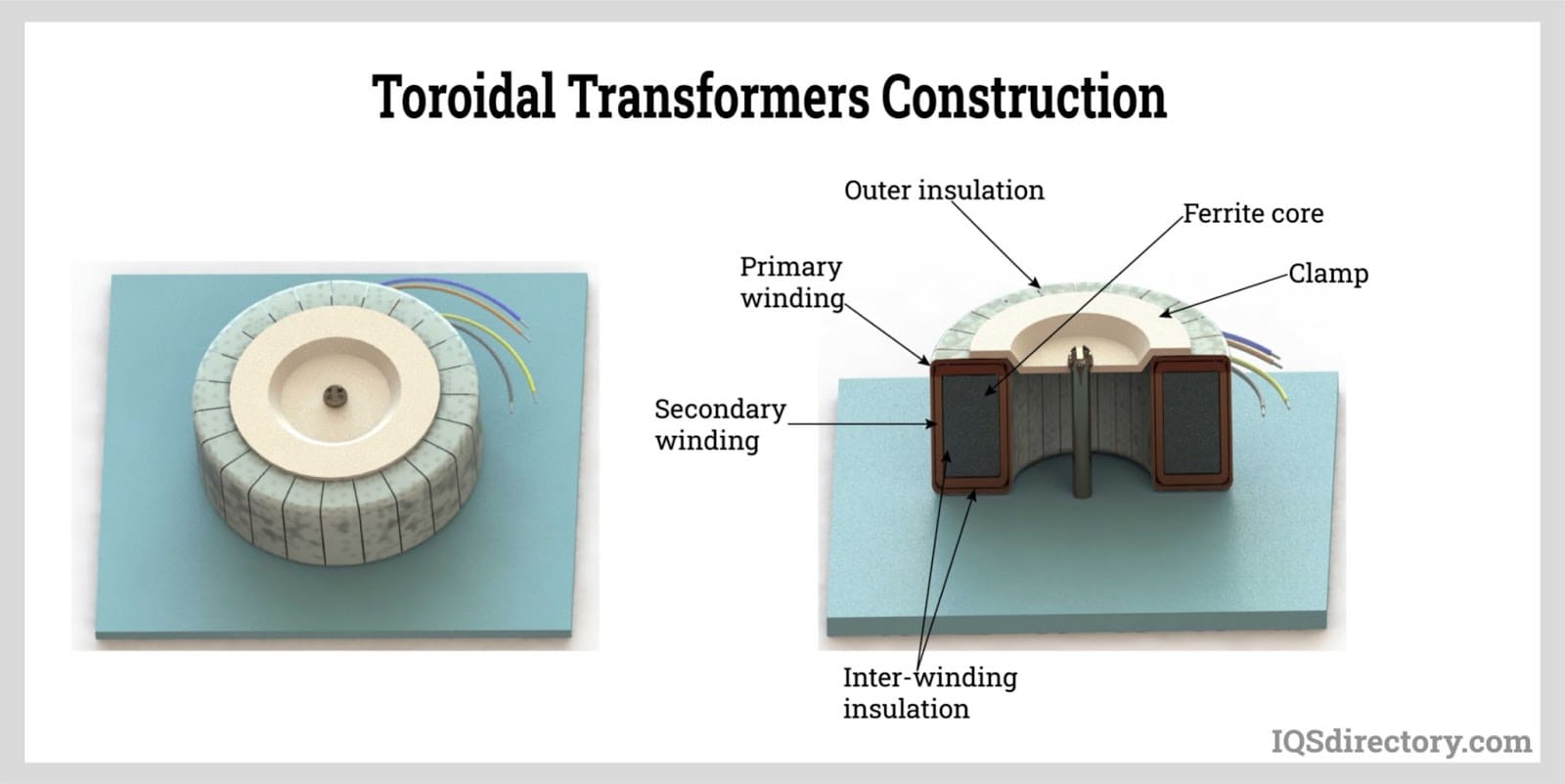
As illustrated in the diagram below, the zig zag transformer typically consists of six coils: three outer coils (zig windings) and three inner coils (zag windings). The outer windings are referred to as "ZIG" windings, while the inner ones are "ZAG" windings.

The core operational principle involves connecting the zig winding of one phase in series with the zag winding of a different phase, thus creating interconnected star windings. In this arrangement, each phase winding is split between two limbs, and two windings with equal turns are wound in opposite directions within each phase. This unique construction allows the transformer to cancel mismatched voltages, especially during unbalanced load conditions or ground faults.
The specific coil connections for a three-phase zig zag transformer are as follows:
- The phase 'a' outer (zig) coil is connected in series with the phase 'b' inner (zag) coil.
- The phase 'b' outer (zig) coil is connected in series with the phase 'c' inner (zag) coil.
- The phase 'c' outer (zig) coil is connected in series with the phase ‘a' inner (zag) coil.
The second terminals of the inner coils are interconnected and brought out as the neutral terminal. This connection enables the passage of zero-sequence current components, which are critical during ground faults or unbalanced loading. Notably, a 30-degree phase shift can occur between the zag winding and the associated line-to-neutral voltage when the windings are interconnected in this manner.
To achieve voltage magnitudes comparable to traditional transformers, the zig zag winding requires approximately 15.47% more turns. While this increases the initial cost, the operational advantages and specialized applications of zig zag transformers often justify the investment, particularly in industrial power distribution, data centers, and critical infrastructure facilities.
Key Applications of Zig Zag Transformers
Zig zag transformers are widely deployed across a variety of power system applications due to their distinctive electrical properties. Below are some of the most common and high-value use cases:
1. Grounding Transformer (Earthing Transformer)
In three-phase electrical systems, particularly those employing delta (Δ) or ungrounded star (Y) connections, there may be no direct path to ground for fault currents or unbalanced loads. In these scenarios, a zig zag transformer can function as a grounding transformer or earthing transformer by establishing a neutral point for the system.
Delta-connected transformers inherently lack a neutral terminal, which can pose protection and voltage stability challenges. By installing a zig zag grounding transformer, a low-impedance path is created for zero-sequence currents, enabling safe dissipation of fault energy and activation of protective relays.

During a line-to-ground fault, the zig zag transformer provides an artificial neutral, allowing zero-sequence components to return to ground and enabling protective devices to isolate the faulted section. Without a grounded neutral, healthy phase voltages can rise toward line-to-line values, elevating the risk of insulation breakdown or equipment damage. The zig zag transformer mitigates both symmetrical and unsymmetrical faults, reducing voltage stress and safeguarding the power system.
2. Harmonic Suppression and Power Quality Improvement
Power quality is a growing concern in today's electrical networks, especially with the proliferation of non-linear loads such as variable frequency drives (VFDs), industrial rectifiers, and electronic equipment. These loads generate harmonics—particularly third-harmonic currents—that can circulate within the network, causing transformer overheating, relay malfunctions, and equipment degradation.
Zig zag transformers are designed to trap and suppress these third-harmonic currents. Due to their interleaved winding configuration, harmonics induced in one winding are canceled by opposing harmonics in the paired winding. This feature is especially valuable in data centers, commercial buildings, and industrial plants where sensitive electronic devices are present and power quality is paramount.
3. Power Electronic Converters
Zig zag transformers are frequently used in conjunction with power electronic converters to address issues related to DC magnetization. Incorrect firing angles of silicon-controlled rectifiers (SCRs) and other switching devices can introduce unwanted DC components into transformer windings. In the zig zag design, the opposing windings on each limb cancel out the DC magnetizing component, preventing core saturation and maintaining transformer efficiency.

As a result, zig zag transformers are the preferred choice for industrial automation systems, electric arc furnaces, and renewable energy installations (such as wind or solar farms) that employ large-scale power electronic conversion equipment.
4. Neutral Formation and Unbalanced Load Compensation
Many three-phase systems require a stable neutral connection to accommodate single-phase loads or to balance unbalanced loads. By using a zig zag transformer, a neutral point can be created in systems that otherwise lack one, such as delta-connected setups. This enables the safe and reliable operation of single-phase loads across three-phase networks, a common requirement in commercial buildings, hospitals, and manufacturing plants.
5. Earthing Reference with Fault Current Limiting
When system design calls for controlled earthing, a resistor can be installed at the neutral terminal of the zig zag transformer to limit earth fault current. This feature is essential in applications where the magnitude of fault current must be restricted to protect downstream equipment and minimize arc flash hazards.
The ability of the zig zag transformer to neutralize system harmonics further enhances its value in critical installations where power quality and equipment longevity are top priorities.
Advantages and Benefits of Zig Zag Transformers
- Cost-effective compared to Scott transformers: Zig zag transformers typically have a simpler design and lower cost than Scott-T transformers, making them an economical choice for power system grounding and harmonic mitigation.
- Low impedance to zero-sequence currents: Their unique interleaved winding structure provides a direct, low-impedance path for zero-sequence currents, enhancing ground fault protection.
- Harmonic voltage suppression: The opposing winding configuration cancels out third-harmonic currents, improving overall power quality and reducing transformer heating.
- Electrical isolation: Zig zag transformers provide effective isolation between the ground and system components, reducing the risk of circulating ground currents and stray voltage problems.
- Delta transformer neutralization: They enable delta-connected transformers to supply a stable neutral point, facilitating the connection of single-phase loads and trapping third-harmonic currents within the phase winding.
- No phase shift between main and secondary windings: Delta–zig zag transformers function similarly to star–star and delta–delta transformers, making them adaptable to a wide range of electrical systems.
- Lower internal impedance: Compared to star-connected transformers, zig zag transformers offer lower internal impedance, which can result in improved system stability and reduced voltage drop during faults.
- Enhanced power system resilience: By managing unbalanced loads and mitigating voltage fluctuations, zig zag transformers increase the robustness of industrial, commercial, and utility power networks.
Buyer’s Guide: How to Choose the Right Zig Zag Transformer
Selecting the best zig zag transformer for your application involves careful consideration of several critical factors. Whether you’re an electrical engineer, facility manager, or procurement specialist, understanding these considerations will help you make a well-informed decision that maximizes safety, performance, and cost-effectiveness:
- System voltage and current ratings: Match the transformer’s voltage and current ratings to your system’s requirements to ensure compatibility and optimal performance.
- Intended application: Are you using the transformer for grounding, harmonic suppression, power quality improvement, or unbalanced load compensation? The specific use case will influence the required transformer design.
- Impedance requirements: Evaluate the desired impedance to zero-sequence currents, as this affects fault current flow and system protection coordination.
- Short-circuit withstand capability: Ensure the transformer can handle expected fault currents without risk of damage or excessive temperature rise.
- Physical size and installation constraints: Consider available space, cooling requirements, and ease of integration into your existing switchgear or substation layout.
- Compliance and certification: Verify that the transformer meets relevant IEC, IEEE, ANSI, or local standards for electrical safety and performance.
- Manufacturer reputation and support: Select a trusted zig zag transformer manufacturer or supplier with proven expertise, quality assurance programs, and responsive customer service.
- Customization options: Some applications may require special features such as forced-air cooling, temperature monitoring, or enhanced insulation systems—consult with suppliers for custom-engineered solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) About Zig Zag Transformers
-
What is the main purpose of a zig zag transformer?
Zig zag transformers are primarily used for system grounding, neutral formation, and harmonic suppression in three-phase electrical systems. -
Can a zig zag transformer be used in renewable energy systems?
Yes, zig zag transformers are increasingly used in wind power plants, solar farms, and other renewable installations to improve grounding, balance unbalanced loads, and suppress harmonics generated by inverters and power converters. -
How does a zig zag transformer improve power quality?
By trapping and canceling third-harmonic currents, zig zag transformers reduce voltage distortion and transformer heating, thereby enhancing overall power system quality. -
What factors should I consider when selecting a zig zag transformer supplier?
Assess technical capability, product range, customization options, after-sales support, and certifications to ensure a reliable and long-lasting solution. -
Where can I find trusted zig zag transformer manufacturers?
Explore our comprehensive directory of zig zag transformer suppliers for verified providers, company profiles, and direct inquiry options.
Comparing Zig Zag Transformers to Alternative Solutions
When investigating grounding and harmonic mitigation solutions, buyers often compare zig zag transformers to other transformer types such as Scott-T transformers, autotransformers, and standard star or delta-wound units. Zig zag transformers stand out for their unique ability to create a neutral point without significant phase shift, superior third-harmonic suppression, and adaptability to a broad range of industrial and utility applications.
If you’re looking to replace legacy grounding transformers, upgrade your power distribution system for improved power quality, or address new compliance requirements, researching zig zag transformer features and use cases is essential. For a side-by-side comparison of zig zag vs. Scott-T or autotransformers, contact our technical experts for guidance.
Popular Industries and Use Cases for Zig Zag Transformers
- Industrial manufacturing facilities: Steel mills, refineries, and chemical plants require robust grounding and harmonic control for large motor loads and sensitive automation equipment.
- Commercial buildings: High-rise offices, hospitals, and data centers use zig zag transformers for neutral formation and power quality assurance in mixed-load environments.
- Utilities and substations: Electric utility companies employ zig zag transformers in substations to stabilize voltage, protect against ground faults, and manage unbalanced loads.
- Renewable energy installations: Wind farms, solar plants, and battery storage sites integrate zig zag transformers to address unique grounding and harmonic challenges associated with power electronic converters.
- Critical infrastructure: Airports, transportation hubs, and water treatment plants rely on zig zag transformers for continuous operation and electrical safety.
How to Choose the Correct Zig Zag Transformer Company
To ensure optimal results when purchasing zig zag transformers, it’s essential to compare multiple suppliers and manufacturers. Our zig zag transformer supplier directory offers a curated list of leading providers, each with a detailed business profile outlining their technical expertise, manufacturing capabilities, and specialization in transformer solutions.
Use our interactive website previewer to evaluate each supplier’s offerings, certifications, and project experience. When you’re ready to request more information or a personalized quote, simply fill out our easy-to-use RFQ form to contact several zig zag transformer companies simultaneously. This streamlined process allows you to compare pricing, product features, lead times, and after-sales support—empowering you to make the most informed decision for your electrical system needs.
Ready to advance your project? Request a quote or contact our transformer experts for assistance in selecting the ideal zig zag transformer for your application.





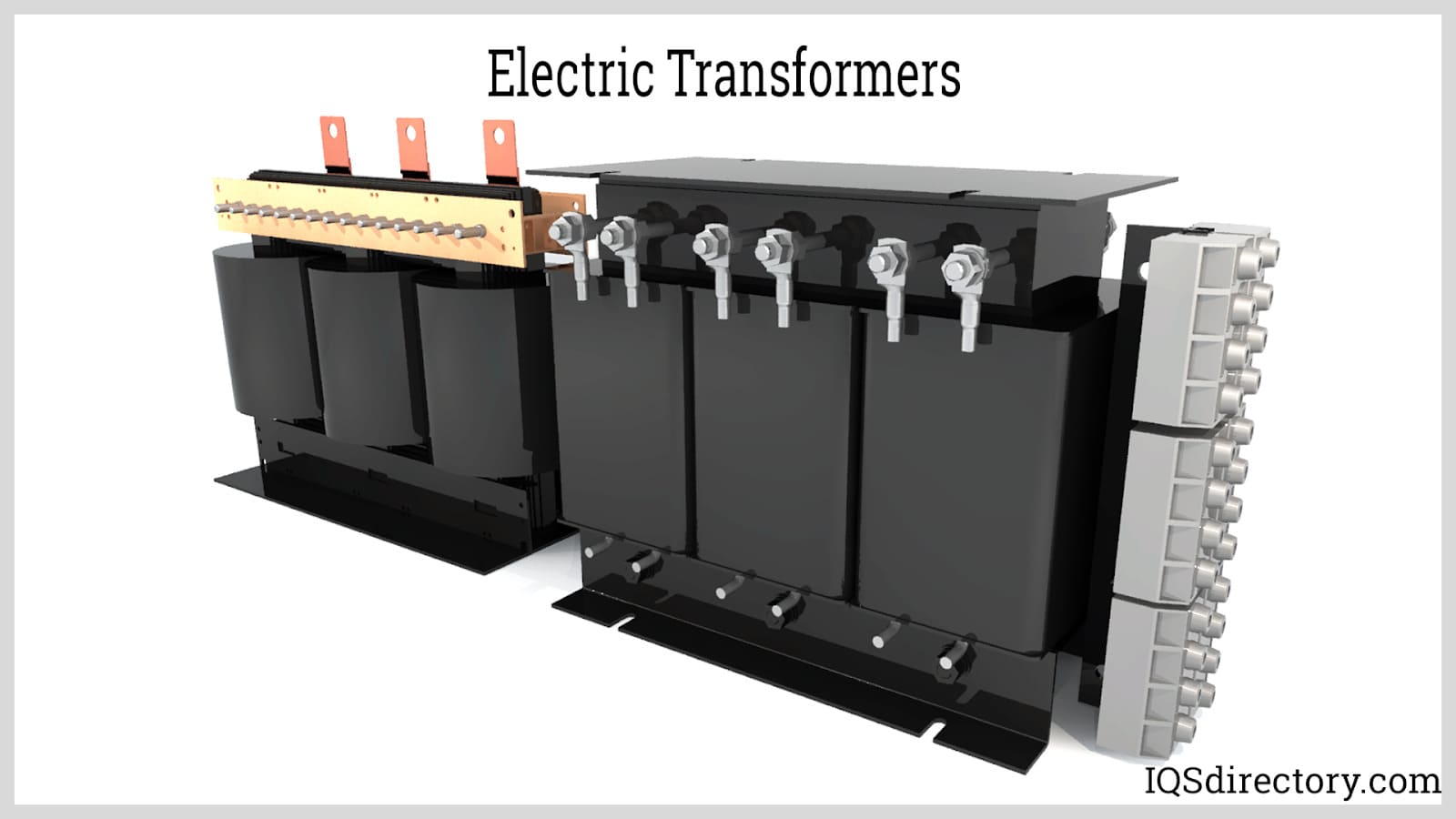





 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services