An isolation transformer offers both physical and electrical separation between two circuits. It isolates the electronic circuits from the main lines and safeguards people against electrical shock. Through magnetic coupling, electrical energy is transferred from the primary to the secondary. Transformers used exclusively as isolation transformers have a ratio of 1:1. Isolation transformers observe the principle of magnetic induction. Magnetic induction utilizes a magnetic field to generate electromagnetic fields (EMF) in a different circuit without changing the frequency. Read More…
With more than 500 current transformer manufacturers in the world, Triad Magnetics realizes you have a choice. Why choose Triad? Having served the needs of many industries for more than half a century, Triad believes its experience makes the difference. And if there is one point experience has taught it, it is that it must remain flexible and adaptable to the changing needs of the market.
At CES Transformers, we dedicate ourselves to designing and manufacturing high-quality electric transformers that power industrial, commercial, and utility applications across the nation. We take pride in combining advanced engineering with decades of hands-on expertise to deliver reliable performance and lasting value. Every transformer we build reflects our commitment to precision, safety, and...

At Spang Engineered Solutions, we specialize in designing and manufacturing high-performance electric transformers that meet the demands of today’s advanced power and control systems. We take pride in engineering solutions that go beyond standard components, combining innovation and precision to deliver superior magnetic and electronic performance.

Established in 1973 manufacturing a wide variety of custom transformers and inductors. Transformer products range from small PC transformers to single-phase units with capacities between 10mW and 25KVA, as well as three-phase transformers from 7VA to 75KVA.

At Olsun Electrics Corporation, we specialize in crafting high-quality electric transformers designed to meet the diverse needs of our customers. Our expertise extends to providing comprehensive solutions that encompass design, manufacturing, and testing, ensuring that every transformer we produce delivers exceptional performance and reliability.
More Isolation Transformer Manufacturers

Isolation Transformers: Essential Guide for Applications, Benefits, and Buying Considerations
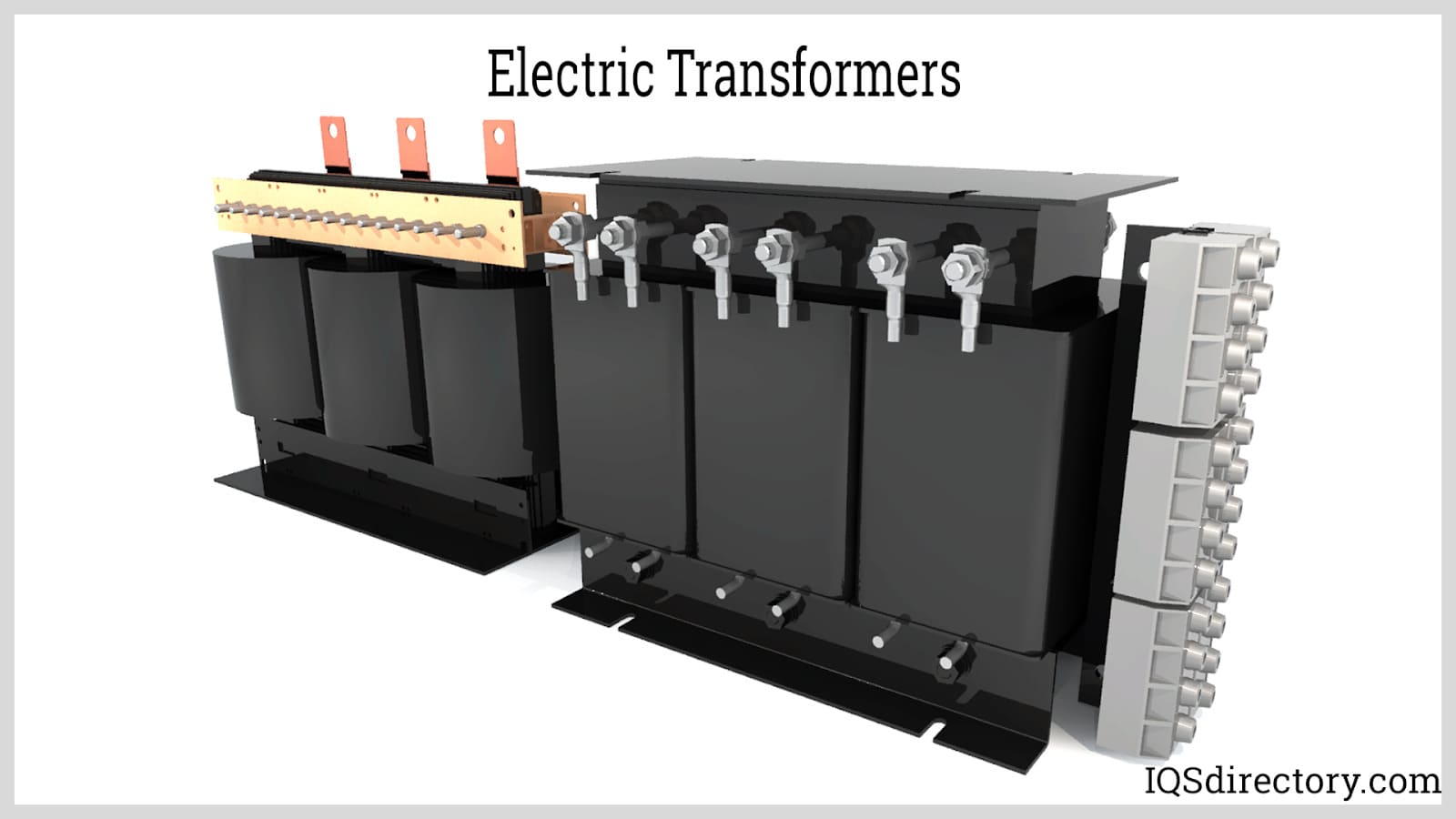
An isolation transformer is an electrical transformer that features electrically isolated primary and secondary windings. This crucial component is widely used in power transmission and distribution networks to provide galvanic isolation, enhance electrical safety, and protect sensitive equipment from voltage spikes, surges, and electrical noise. By decoupling the input and output circuits, isolation transformers help ensure reliable power delivery, safeguard end-user devices, and minimize risks associated with ground loops and electrical interference.
What Is an Isolation Transformer and How Does It Work?
At its core, an isolation transformer transfers electrical power from an alternating current (AC) source to a connected device or system while preventing direct electrical connection between the input and output circuits. This is achieved through separate windings and robust insulation—unlike auto transformers, which share a common winding and do not offer full isolation.
The main purpose of an isolation transformer is to reduce voltage peaks and spikes that can occur due to lightning strikes, static discharge, fluctuations in the electrical grid, or switching events. These voltage transients can damage sensitive electronic equipment, disrupt industrial automation, or interfere with medical devices. By including an isolation transformer in your power distribution system, you can effectively suppress such disturbances and maintain continuous, high-quality power delivery.

When voltage spikes—ranging from a few volts to several thousand volts—travel along the power supply lines, they pose a risk to connected loads. Isolation transformers employ electrostatic shielding and magnetic coupling to block or attenuate these unwanted signals, providing a safe power environment. This is why they are a critical part of electrical infrastructure in hospitals, data centers, manufacturing plants, and commercial buildings.
Types of Isolation Transformers: Which One Suits Your Needs?
There are several types of isolation transformers, each engineered for specific applications and operational requirements. Understanding the differences can help you select the right transformer for your facility or equipment. Below are the most widely used variants:
Constant Voltage Transformer (CVT)
A constant voltage transformer (CVT) is designed to deliver a stable, regulated output voltage regardless of input voltage fluctuations. CVTs use ferroresonant technology, combining a tank circuit with a high-voltage winding and a capacitor to maintain consistent output. This makes them invaluable in environments where voltage stability is vital, such as laboratories, industrial automation, and telecommunications.

Unlike conventional voltage stabilizers, CVTs do not rely on relays, eliminating brief interruptions and reducing maintenance. The built-in energy storage and unique winding design offer superior protection against surges and spikes, making these transformers popular for protecting mission-critical electronics, CNC machinery, and sensitive measurement instruments.
Ultra-Isolation Transformer
An ultra-isolation transformer is engineered to eliminate all forms of electrical noise, including common-mode and transverse-mode noise. These transformers are essential in applications where electronic noise can affect performance or safety, such as in pulse transformer circuits, medical equipment, audio systems, and digital communications.
Ultra-isolation transformers feature enhanced insulation between primary and secondary windings, often tested to withstand voltages from 1000 to 4000 volts. Specialized shielding techniques further suppress noise, while a split-neutral secondary allows for a separately derived source—combating ground loops and improving electromagnetic compatibility (EMC).

Drive Isolation Transformer
A drive isolation transformer supplies power to variable frequency drives (VFDs) and other AC/DC drive systems. These transformers provide both voltage adaptation and robust isolation, protecting sensitive drive electronics from grid disturbances, harmonics, and line transients. They are critical in motor control centers, conveyor systems, and industrial automation environments.

The design of drive isolation transformers accounts for the mechanical and electrical stresses introduced by SCR drives and other power electronics, ensuring reliability and long service life. If you’re researching motor drive transformers or industrial isolation transformer solutions, be sure to evaluate products with enhanced harmonic filtering and surge protection features.
Galvanic Isolation Transformer
Galvanic isolation transformers are specialized for minimizing ground loop noise and isolating equipment from ground voltage differences. These transformers are frequently used in uninterruptible power supply (UPS) systems, audio installations, and sensitive computer networks. By isolating the power conductors—but not the ground wire—they help eliminate common-mode noise and reduce the risk of signal interference or equipment malfunction.
Some UPS systems offer galvanic isolation as an optional feature. If you’re comparing UPS systems, check whether galvanic isolation is included or available as an add-on, especially for applications requiring high reliability and data integrity.
Isolation Transformer Applications: Where Are They Used?
Isolation transformers are used across a wide range of industries and environments where power quality, safety, and equipment protection are paramount. Key applications include:
- Electrical noise protection: Shield circuits from ground loop interference and electromagnetic interference (EMI), vital in audio studios, laboratories, and IT networks.
- Safety separation: Provide galvanic isolation in power supplies, medical devices, and industrial control panels to prevent accidental electrical shock and equipment failure.
- Voltage adaptation: Enable safe transfer of power between circuits with differing voltage levels—critical in international equipment deployments and retrofitting older systems.
- Industrial automation: Protect programmable logic controllers (PLCs), CNC machines, and robotics from voltage surges and electrical noise.
- Medical and laboratory equipment: Ensure patient and operator safety by isolating sensitive diagnostic or therapeutic devices from electrical faults.
- Computer network protection: As pulse transformers, isolation units safeguard data centers, server rooms, and communication hubs from surges and impulse noise.
- Lightning and surge protection: Defend against impulse noise, strong lightning events, capacitor discharges, and bus short-circuit faults, preserving uptime and minimizing costly downtime.
- Uninterruptible power supplies (UPS): Enhance the reliability and performance of backup power systems, especially in mission-critical IT and healthcare applications.
Benefits of Using Isolation Transformers
Investing in a high-quality isolation transformer delivers a range of technical and operational advantages, including:
- Improved power quality: Smooths out voltage fluctuations, suppresses transients, and delivers consistent power to sensitive devices.
- Noise reduction: Minimizes electromagnetic and radio frequency interference (RFI/EMI), essential for data integrity, audio clarity, and high-precision electronics.
- Enhanced safety: Reduces risk of electrical shock by isolating circuits, protecting users and maintaining compliance with industry standards (such as IEC, UL, and NEC).
- Fault and surge protection: Safeguards equipment from damage caused by overvoltages, spikes, and short circuits.
- Harmonics mitigation: Filters harmonic distortions generated by non-linear loads like VFDs, improving overall system efficiency and lifespan.
- Earthing failure prevention: Prevents ground faults from propagating through interconnected equipment, reducing downtime and repair costs.
- System flexibility: Allows for modular, scalable power distribution in complex installations such as manufacturing plants, research labs, and data centers.
Potential Drawbacks: What Are the Disadvantages of Isolation Transformers?
While isolation transformers offer substantial benefits, it is important to be aware of their limitations and potential trade-offs:
- Core saturation with DC pulses: If operated with DC signals, the transformer core may saturate, diminishing performance and efficiency.
- Higher cost: Due to specialized design, insulation, and shielding requirements, isolation transformers are generally more expensive than standard transformers.
- Low-frequency distortion: When used as a pulse transformer at low frequencies, the output waveform may become distorted, potentially impacting sensitive applications.
- Increased size and weight: Enhanced insulation and shielding often lead to larger, heavier units compared to conventional transformers.
- Efficiency losses: The added windings and insulation can result in slightly reduced energy efficiency, particularly in smaller or lower-quality units.
How to Choose the Best Isolation Transformer for Your Application
When selecting an isolation transformer, consider your specific application requirements, environmental conditions, and regulatory standards. Here are key factors to guide your decision:
- Voltage and power rating: Ensure the transformer can handle the input and output voltage levels, as well as the total load capacity (in VA or kVA).
- Frequency compatibility: Match the transformer's design with your system’s operating frequency (e.g., 50 Hz or 60 Hz).
- Type and configuration: Choose between single-phase or three-phase isolation transformers based on your facility’s electrical distribution.
- Shielding and noise attenuation: For environments with high EMI/RFI, opt for models with advanced electrostatic shielding and noise suppression features.
- Safety and compliance: Verify certification to standards like UL, IEC, or CSA, especially for medical, industrial, or export applications.
- Thermal performance: Consider cooling requirements and ambient temperature ratings to ensure reliable, long-term operation.
- Custom features: Assess whether you need additional features such as surge protection, monitoring interfaces, or modular scalability.
- Physical footprint: Confirm dimensions and mounting options fit your available installation space.
Are you unsure which isolation transformer matches your needs? Ask yourself: What is the primary use case—industrial, medical, IT, or audio-visual? Do you face specific power quality issues such as harmonics or frequent surges? What are your long-term maintenance and scalability requirements?
Industries and Use Cases: Where Are Isolation Transformers Most Valuable?
Isolation transformers are indispensable in sectors where power quality, reliability, and safety are non-negotiable. Explore some of the top industries and scenarios where isolation transformers deliver critical value:
- Healthcare facilities: Isolation transformers are mandated in operating rooms, intensive care units, and diagnostic labs to isolate life-support equipment and protect patients and operators from electrical faults.
- Industrial manufacturing: Used to stabilize power for PLCs, robotics, welding machines, and precision tools, minimizing downtime and maintenance costs.
- Data centers and server rooms: Shield sensitive IT infrastructure from power disturbances, preventing data loss and hardware damage.
- Broadcast and recording studios: Essential for achieving noise-free audio and video signals by suppressing ground loops and EMI.
- Laboratories and research facilities: Provide clean, isolated power for high-precision instruments, test benches, and measurement systems.
- Commercial buildings: Reduce the risk of electrical fires, ensure compliance with safety codes, and protect elevator systems, lighting, and HVAC controls.
- Renewable energy systems: Isolate solar inverters and battery storage systems from the main grid, supporting safe integration and troubleshooting.
Frequently Asked Questions About Isolation Transformers
What is the difference between an isolation transformer and a regular transformer?
Unlike standard transformers, which may share windings or ground connections, isolation transformers feature complete electrical separation between input and output circuits. This ensures maximum safety, noise suppression, and protection from voltage disturbances.
Can isolation transformers be used for both single-phase and three-phase systems?
Yes! Isolation transformers are available in both single-phase and three-phase configurations, supporting everything from residential equipment to industrial machinery and commercial buildings.
How do I size an isolation transformer?
To properly size an isolation transformer, calculate the total load in volt-amperes (VA) or kilovolt-amperes (kVA), factor in any surge or inrush currents, and select a transformer rated at least 20% above your maximum expected load for reliable performance.
What certifications should I look for when buying an isolation transformer?
Look for certifications relevant to your application and jurisdiction, such as UL Listed, IEC 61558, CSA, or ISO 9001. Medical, industrial, and export applications often require stricter compliance standards.
Where can I buy high-quality isolation transformers?
Explore our directory of isolation transformer suppliers to compare models, features, and pricing from leading manufacturers and distributors.
Buying Guide: How to Choose a Trusted Isolation Transformer Supplier
Selecting the right isolation transformer supplier is as important as choosing the correct product. Here are best practices to guide your procurement process:
- Compare multiple isolation transformer manufacturers and distributors to evaluate product selection, pricing, and customer support.
- Review supplier business profiles for their technical expertise, certifications, and years of experience in the transformer industry.
- Use our contact forms to request technical specifications, custom quotes, or application guidance from suppliers.
- Check out each supplier’s website using our proprietary previewer to assess specialization in your sector (medical, industrial, IT, etc.).
- Leverage our RFQ (request for quote) feature to easily reach multiple isolation transformer businesses with your requirements.
Need help narrowing down your options? Ask these questions when evaluating a supplier:
- Does the supplier offer custom isolation transformer solutions for unique voltage, frequency, or form factor needs?
- What is their track record of on-time delivery and after-sales support?
- Do they provide technical documentation, installation guides, and ongoing maintenance resources?
- Are their products certified to major international standards?
- Can they support volume orders, rapid prototyping, or field service for large-scale projects?
Get Started: Find Your Ideal Isolation Transformer Today
Ready to take the next step? Browse our comprehensive list of isolation transformer suppliers to find the perfect match for your project or application. Whether you’re looking for standard models, custom-built solutions, or expert technical support, you’ll find leading manufacturers and distributors committed to delivering safe, reliable, and efficient power isolation solutions.
For further assistance, use our RFQ form to connect directly with multiple suppliers and receive quotes tailored to your requirements. Our goal is to help you make an informed, confident decision—ensuring your critical systems are protected, compliant, and performing at their best.
Still have questions about isolation transformers, installation best practices, or regulatory compliance? Contact our expert advisors or browse our in-depth resources on power conditioning, surge protection, and electrical safety standards.









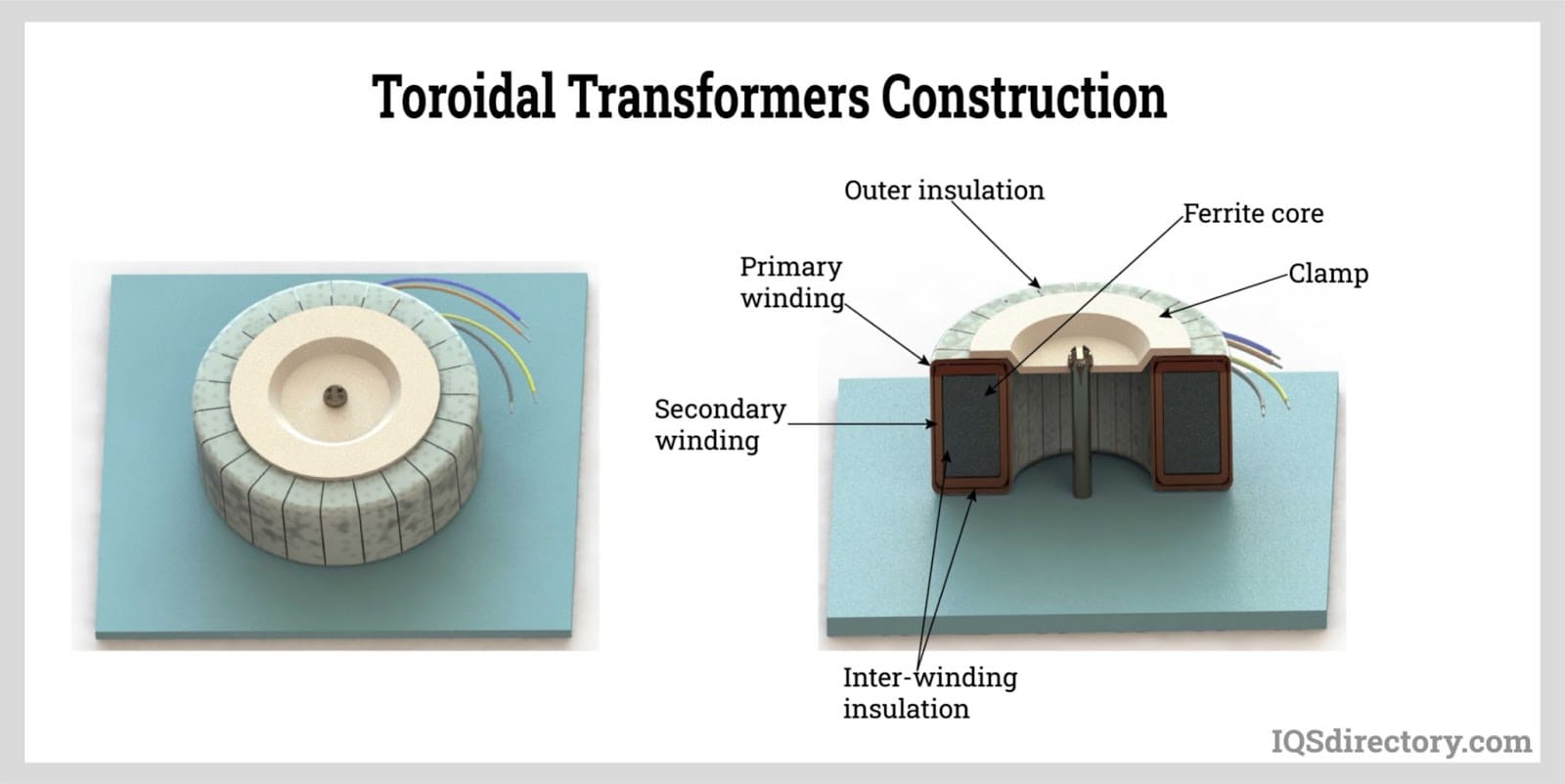

 Electric Coils
Electric Coils Electric Switches
Electric Switches Electric Transformers
Electric Transformers Electronic Connectors
Electronic Connectors Electronic Enclosures
Electronic Enclosures EMI Shielding
EMI Shielding Membrane Switches
Membrane Switches Power Cords
Power Cords Static Eliminators
Static Eliminators Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services